Overview
The multibias package is used to adjust for multiple biases in causal inference when working with observational data. Bias here refers to the case when the associational estimate of effect does not equal the causal estimate of effect:
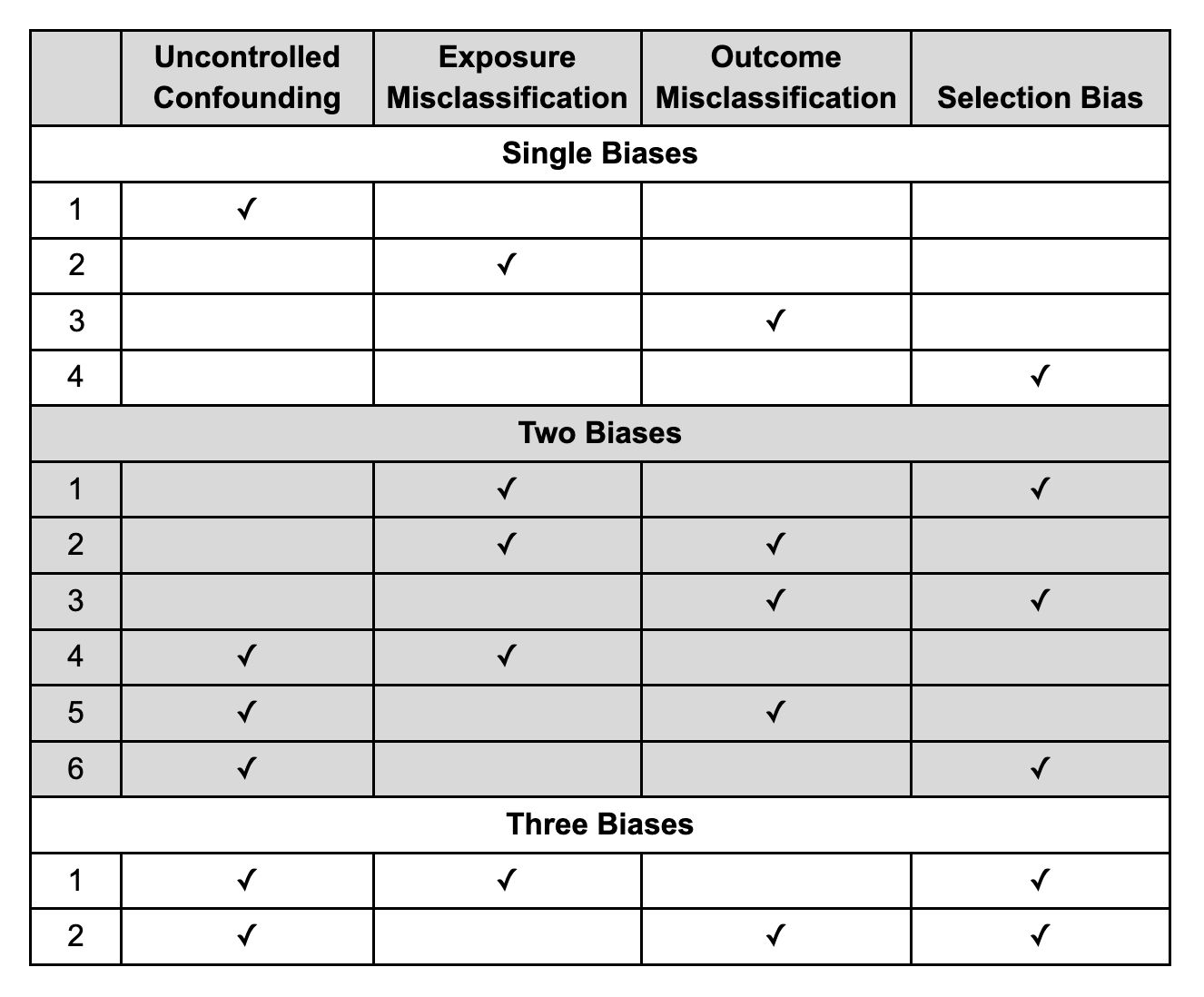
The multibias_adjust() function outputs odds ratio estimates adjusted for any combination of: uncontrolled confounding (uc), exposure misclassification (em), outcome misclassification (om), and selection bias (sel).
The package also includes several dataframes that are useful for validating the bias adjustment methods. Each dataframe contains different combinations of bias as identified by the same prefixing system. For each bias combination, there is a dataframe with incomplete information (as would be encountered in the real world) (e.g., df_uc) and a dataframe with complete information that was used to derive the biased data (e.g., df_uc_source).
Installation
# install from CRAN
install.packages("multibias")
# install from github using devtools
# library("devtools")
devtools::install_github("pcbrendel/multibias")Getting started
- Represent the observed causal data as a
data_observedobject. Here you provide the data, specify the key variables, and list the biases present in the data. See list below for the different bias combinations that multibias can handle. - Obtain one of the two sources for bias adjustment:
- Bias parameters - via the
bias_paramsobject. Values for these parameters could come from the literature, validation data, or expert opinion. Each parameter can be represented as a single value or as a probability distribution. See thebias_paramsdocumentation for the full bias models. - Validation dataframe - via the
data_validationobject. The purpose of validation data is to use an external data source to transport the necessary causal relationships that are missing in the observed data.
- Bias parameters - via the
- Run
multibias_adjust()using the above inputs to obtain the bias-adjusted exposure-outcome odds ratio and confidence interval. - Visualize a Forest Plot of the observed effect estimate against various bias-adjusted estimates via
multibias_plot().
References
- Brendel PB, Torres AZ, Arah OA, Simultaneous adjustment of uncontrolled confounding, selection bias and misclassification in multiple-bias modelling, International Journal of Epidemiology, Volume 52, Issue 4, Pages 1220–1230. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyad001
- Wood CJC, Tilling K, Bartlett JW, Hughes RA. Quantitative bias analysis for mismeasured variables in health research: a review of software tools. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2025 Aug 1;25(1):187. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-025-02635-w